Introduction
Rapid diagnostic technologies for infectious diseases have revolutionized the healthcare industry. These tests provide prompt and accurate results, enabling prompt treatment and disease containment for contagious illnesses. In this blog post, we will look at the significance of rapid testing, its technology and applications, and its implications for public health.
The Need for Rapid Tests
The threat that infectious illnesses represent to world health is substantial. Effective patient management and outbreak control depend on a prompt and precise diagnosis. Long laboratory processes are frequently involved in conventional diagnostic techniques, which can delay treatment and raise the risk of disease transmission. Rapid tests solve this issue by giving answers in a matter of minutes or hours, allowing for quick decision-making and halting the spread of disease.
Technology Behind Rapid Tests
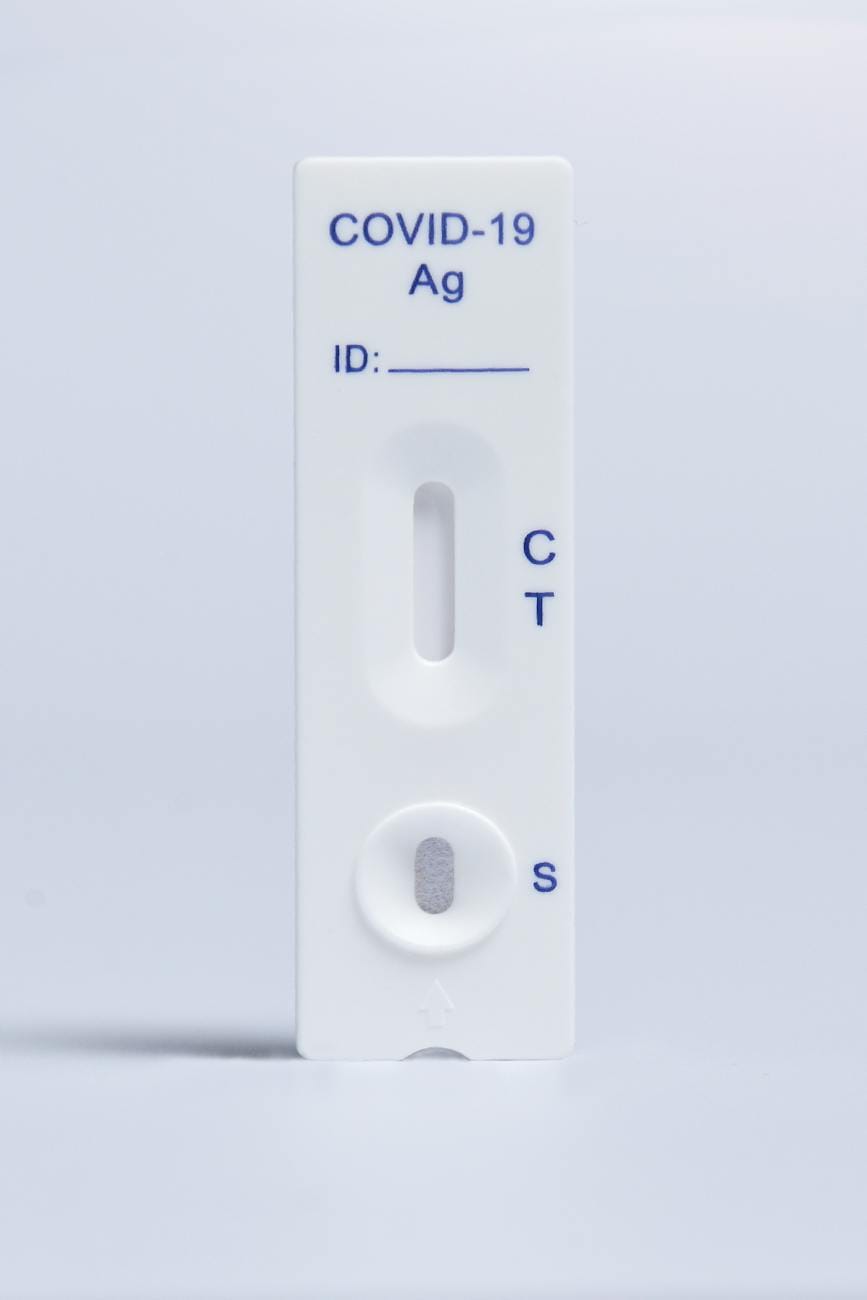
- Antigen Tests: Antigen testing finds particular proteins on a pathogen’s surface, like a virus. They are particularly useful for diagnosing acute infections. The quick antigen test for COVID-19, which yields results in as little as 15–30 minutes, is one prominent example.
- Nucleic Acid Tests: PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and isothermal amplification assays are two examples of nucleic acid tests that can be used to identify pathogens’ genetic material (DNA or RNA). Despite having higher sensitivity and specificity than antigen tests, they frequently call for more specialized equipment and take longer to deliver findings.
- Serological Tests: Serological examinations look for antibodies that the body produces in response to an infection. These tests are useful for locating previous infections or checking the efficacy of vaccinations.
Applications of Rapid Tests
- Point-of-Care Testing: Rapid tests are ideal for point-of-care settings, such as clinics, doctor’s offices, and remote areas with limited access to traditional laboratories. Healthcare providers can quickly assess a patient’s infection status and determine the appropriate course of action.
- Mass Screening: Rapid tests used in mass screening during outbreaks can help quickly identify and isolate affected people, stopping further spread. Using this strategy has been essential in treating illnesses like COVID-19.
- Emergency Response: Rapid tests play a vital role in emergency response situations, such as natural disasters or bioterrorism events, where rapid diagnosis is essential to contain the spread of infectious agents.
- Travel and Border Control: Rapid testing has become a standard part of entrance procedures for many nations, assisting in the fight against the importation of infectious diseases.
Impact on Public Health
- Early Detection: Early detection of infectious diseases is made possible by rapid tests, allowing for fast treatment and a reduction in the severity of illnesses.
- Containment: Swift identification of infected individuals through rapid testing facilitates effective contact tracing and isolation measures, helping to contain outbreaks.
- Resource Conservation: Rapid tests reduce the burden on healthcare facilities and resources, as they require minimal equipment and can be performed by non-specialized personnel.
- Improved Surveillance: Rapid testing improves disease surveillance efforts by supplying real-time data on illness prevalence, empowering authorities to make wise decisions.
Challenges and Limitations
While rapid tests have revolutionized infectious disease diagnostics, they are not without challenges:
- Sensitivity and Specificity: When compared to conventional laboratory techniques, some rapid tests may have reduced sensitivity and specificity, which can result in false-positive or false-negative results.
- Availability: Rapid test accessibility continues to be problematic, especially in areas with limited resources.
- Quality Control: Maintaining the quality and reliability of rapid tests, especially when produced at a large scale, is crucial to avoid inaccuracies.
Conclusion
Infectious illness rapid diagnostic tests have changed the healthcare landscape by providing quick, easy, and dependable methods for disease detection and management. It is impossible to overstate their influence on public health, particularly during outbreaks. As technology continues to advance, the development of more accurate and widely accessible rapid tests will further enhance our ability to respond to infectious diseases effectively. Undoubtedly, these tests will continue to be a key component of our efforts to protect world health.